In the modern world, most manufacturers opt for CNC prototyping when it comes to the manufacture of parts and products in large quantities. CNC machines are vital for the completion of the CNC machining process.
The manufacturing process uses computer inputs to control vital parts of the machining tools such as lathes and drills. The machining technique is used across various industries to create end-use parts and prototypes.
The whole process begins with a digital 3D design that is created using 3D software, which in turn the computer will translate into commands and instructions for the cutting tools. The instructions are commonly known as G-code.
Once the code is fed onto the machine, there is little supervision or operators will be required to monitor the manufacturing process since all the cutting and performance are completely autonomous.
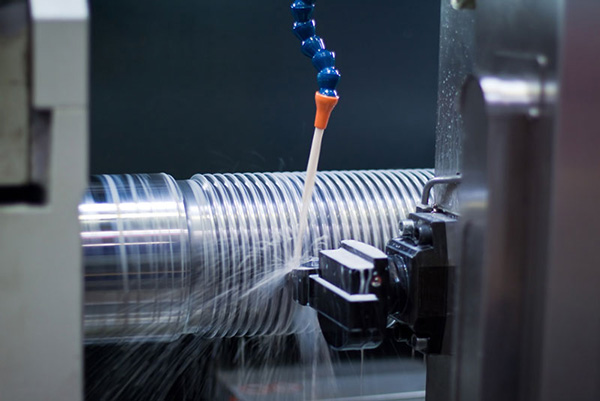
Precision CNC turning, *picture from expert-cnc.co.uk
Is The CNC Machining Process Best For Prototyping
Even though 3D printing is the most dominant and widely used technique of rapid prototyping, CNC machining also gives it a run for its money when it comes to the manufacture of products/prototypes.
To understand the techniques and forms of the prototypes, its vital we first understand why do these prototypes exist in the first place? First, prototypes have a wide range of functions with the most basic one being a representation of how the final product will look, feel, or appear.
The visual representation will act as a guide for the research and development department and show proof-of-concept; if the prototype has excellent aesthetics they can be used in a sales pitch to new or potential investors.
For other types of prototypes, there use is more than visual representation. Dependent on the phase of the product development, firms will need to create production or engineering prototypes that not only look like the final product but function like it too.
In reality, 3D printing is an excellent option for the production of prototypes that are similar to the final part but for functional prototypes, CNC prototyping is the most preferred technique for parts/prototypes that require higher dimensional stability as well as strength.
In the long-run, not a lot of manufacturers use end-use parts made from 3D printing. CNC machining is a perfect choice but the suitability depends on the nature and type of the prototype.
Between Conventional and CNC Prototyping Which Is Better?
Both CNC prototyping and conventional machining, use the same raw-material and produce the same final product but the key differences between the two are:
- The key difference between the two is their nature, conventional machining is manual while CNC prototyping is autonomous.
- CNC prototyping comes a myriad of benefits that cannot be found from conventional toolings such as speed, production rate, and accuracy.
- For CNC prototyping, an operator can execute commands and control from the back of the computer while for conventional machining, the operator uses the entire set-up to get the job done.
- For small quantities, conventional machining costs less but large-scale projects CNC prototyping is the perfect option as they offer huge economies of scale.
